Pigmentation

The term pigmentation refers to the ranges of colour within the skin. Pigmentation can range from simple freckles, age spots and sun spots to large areas of discolouration like in Melasma. There are many causes and types of pigmentation which can be caused by hormones, sun damage, trauma and genetics.
There are special cells called melanocytes in the skin that make melanin, a pigment that controls the colour of our skin. The actual number of melanocytes within our skin is the same regardless of skin type, it is the production of melanin from these cells which determines skin colour. High levels of melanin cause darker skin and lower levels cause lighter skin.
Hypopigmentation refers to areas of lightened skin and hyperpigmentation refers to areas of darkened skin, both are caused by altered levels of melanin. This occurs when the melanocytes are damaged or not functioning adequately, therefore affecting melanin production (either stopping production or increasing production).
Triggers for melanin production such as the sun, heat, injury and hormones cause the melanin to be produced in the deep layers of the skin. The melanin then slowly rises through the layers to the skin to sometimes sit more superficially (such as freckles and sun spots).
This is why some pigmentation is difficult to see and difficult to treat as it sits deep within the dermis of the skin. Melasma is a condition where the melanin can sit both superficial and deep making it much more difficult to treat.
FAQs
What are some common types of pigmentation?
Freckles
Often genetic but can be triggered by heat and sun exposure.
Sunspots or solar lentigos
Occur as a result of chronic sun exposure and sun damage.
Diffuse sun damage
Occurs due to chronic sun exposure, solarium use, tanning and occupational sun exposure. This will cause skin colour irregularities with patches of hypo and hyperpigmentation.
Age spots
These results from sun exposure and age related changes in melanin production.
Melasma
Results from multifactorial causes ranging from hormones to genetics and is triggered by heat and sun exposure. Melasma is difficult to treat but can be controlled through regular treatments.
Post inflammatory hyper or hypopigmentation
Post inflammatory pigment changes can occur to the skin after a trauma, as a result of excess melanin being produced by means of protection.
Vitiligo (hypopigmentation)
This is an autoimmune disease resulting in patches of hypopigmentation.
How is pigmentation/photoageing classified?
Disorders of pigmentation are primarily caused by trauma to the skin in the form of sun damage and UV exposure, injury and inflammation as well as hormonal, medications and underlying medical causes.
The most common causes we see in Australia is hyperpigmentation as a result of sun exposure, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation and Melasma (hormonal pigmentation).
Sun exposure
Melanin functions to protect the skin cells from UV damage however chronic sun exposure, frequent sunburns, tanning and solarium use will result in underlying cellular changes resulting in an increase in melanin. This results in damaging effects such as reduced collagen and elastin, decreased skin laxity, poor texture, accelerated ageing and of course the risk of cancer.
Trauma
Trauma or injury to the skin can result in hyper or hypopigmentation. The most common is hyperpigmentation due to inflammation which in turns triggers the production of melanin as a means of protecting the skin. This is especially common in darker skin types where there is already an excess of melanin. A common cause of post inflammatory hyperpigmentation is inflammatory acne, abrasions or surgical wounds, bites, burns, IPL/BBL or laser treatments and deep chemical peels which cause injury to the top layers of the skin.
Hormones
Hormone imbalances, pregnancy, breastfeeding and certain medications such as the oral contraceptive pill can result in melasma which is an overproduction of melanin at both superficial and deep layers of the skin.
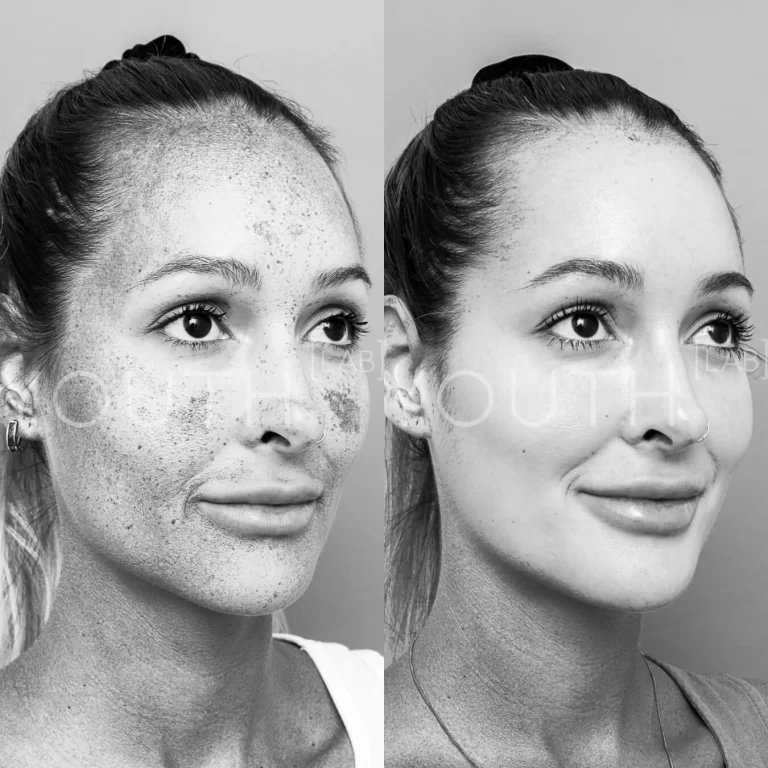
How do we treat pigmentation at Youth Lab?
As with many skin conditions that are triggered by UV and sun exposure, the main focus of treatment is to prevent damage and repair damage by strict sun avoidance.
Pigmentation treatments also focus on preventing the occurrence of new pigmentation by avoiding and removing the triggers.
Key triggers include sun exposure and hormones, removal or reduction in existing pigmentation through lightening treatments and removing superficial pigmentation and finally the prevention of ongoing hyperpigmentation by inhibiting the melanocytes and preventing further melanin production,
The primary prevention method is to avoid exposure to UV radiation. This includes daily use of a broad spectrum SPF 50, use of protective measures such as a hat as well as avoidance of the sun in peak times and using shade as much as possible. It goes without saying that sun tanning and use of sunbeds should be avoided.
It is also important for those with a known underlying cause such as hormonal imbalance, that this be treated optimally.
Topical treatments are also essential and will be prescribed for all types of pigmentation. These cosmeceutical brightening and lightening creams contain ingredients which help to slow down melanin production and lighten existing pigmentation. Some ingredients include hydroquinone, retinoic acid, vitamin C and Kojic acid. The use of cosmeceutical lightening creams are needed prior to any depigmentation treatment for a minimum of 2 weeks.
What are our recommended treatments?
As with many of the treatment recommendations at Youth Lab, a combination of treatments may be required for optimal results.
Please note that the below recommended treatments are a reference point and full treatment recommendations will be made following a consultation.
BBL Corrective
Broadband Light can effectively treat pigmentation, freckles, sun spots, lentigos, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and irregular skin tone.
Halo Laser
Halo Laser is used to treat all types of pigmentation from sun damage, freckles, hormonal pigmentation and uneven skin tone. It can be combined with BBL for optimal results.
Dermamelan
Dermamelan is the gold standard topical treatment for melasma and pigmentation. It is a mask application containing active ingredients which work to suppress melanin production, reduce the appearance of melanin and prevent recurrence of pigmentation.
Skin Needling
Skin needling with brightening and pigment inhibiting serum infusions can help with superficial pigmentation, epidermal melasma and sun damage.
Clinical Peels
Peels are a fantastic way to treat both superficial pigmentation from sun damage, deeper melasma and also post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Chemical peels cause exfoliation of the superficial to mid layers of the skin.
Hydrafacial
Hydrafacials can help with exfoliation of superficial pigment as well as the infusion of antioxidants and brightening serums to inhibit melanin formation.